Sass安装、查测及更新
安装Sass
先下载安装Rubyhttp://rubyinstaller.org/downloads
然后打开电脑的命令终端,输入下面的命令:
gem install sass
查看Sass版本
sass -v
更新Sass
gem update sass
卸载Sass
gem uninstall sass
Sass编译
.scss文件编译为.css文件
sass test.scss test.css
编译风格
Sass提供四个编译风格选项
- nested:嵌套缩进的css代码,它是默认值。
- expanded:没有缩进的、扩展的css代码。
- compact:简洁格式的css代码。
- compressed:压缩后的css代码。
sass --style compressed test.sass test.css
Sass监听
可以让Sass监听某个文件或目录,一旦源文件有变动,就自动生成编译后的版本。
// watch a file
sass --watch input.scss:output.css
// watch a directory
sass --watch app/sass:public/stylesheets
Sass基本语法
变量
变量声明
$blue : #1875e7;
div{
color : $blue;
}
编译后的css代码
div{
color : #1875e7;
}
默认变量
在变量值后面加上!default即为默认变量
$baseLineHeight: 2;
$baseLineHeight: 1.5 !default;
body{
line-height: $baseLineHeight;
}
在默认变量前后重新声明该变量,会覆盖默认值。
编译后的css代码
body{
line-height:2;
}
全局变量与局部变量
全局变量: 在选择器、函数、混合宏…的外面定义的变量
局部变量: 在选择器、函数、混合宏…的里面定义的变量
局部变量就成为了全局变量的影子。局部变量只会在局部范围内覆盖全局变量。
$color: orange !default; //定义全局变量
.block {
color: $color; //调用全局变量
}
em {
$color: red; //定义局部变量
a {
color: $color; //调用局部变量
}
}
span {
color: $color; //调用全局变量
}
编译后的css代码
.block {
color: orange;
}
em a {
color: red;
}
span {
color: orange;
}
如果变量需要镶嵌在字符串之中,就必须需要写在#{}之中。
$side : left;
.rounded {
border-#{$side}-radius: 5px;
}
嵌套
在嵌套的代码块内,可以使用
&引用父元素。
选择器嵌套
nav {
a {
color: red;
header & {
color:green;
}
}
}
编译后的css代码
nav a {
color:red;
}
header nav a {
color:green;
}
属性嵌套
.box {
border: {
top: 1px solid red;
bottom: 1px solid green;
}
}
编译后的css代码
.box {
border-top: 1px solid red;
border-bottom: 1px solid green;
}
伪类嵌套
a {
&:hover { color: #ffb3ff; }
}
编译后的css代码
a:hover {
color: #ffb3ff;
}
注释
- 标准注释:
/* comment */, 会保留到编译后的文件 - 单行注释:
// comment, 只保留在Sass源文件中,编译后被省略 - 重要注释:
/*! 重要注释*/, 在/*后面加一个感叹号!,即使是压缩模式编译,也会保留这行注释,通常可以用于声明版权信息
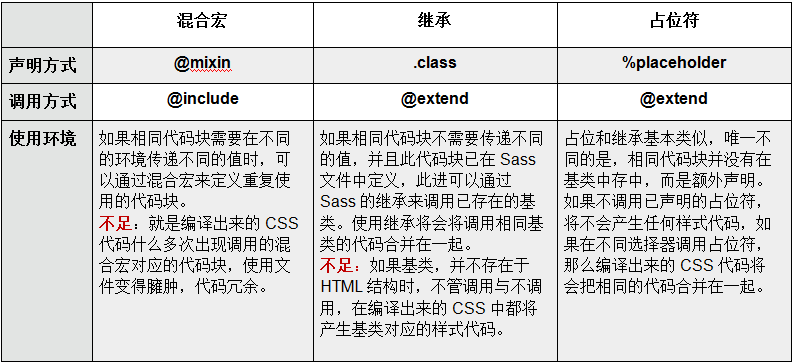
mixin 混合宏
声明不带参数的mixin
@mixin border-radius{
-webkit-border-radius: 5px;
border-radius: 5px;
}
声明带参数的mixin
@mixin border-radius($radius:5px){
-webkit-border-radius: $radius;
border-radius: $radius;
}
调用mixin
关键词@include来调用声明好的mixin
button {
@include border-radius;
}
mixin 的参数
传一个不带值得参数
@mixin border-radius($radius){
-webkit-border-radius: $radius;
border-radius: $radius;
}
在调用的时候可以给这个mixin传一个参数值:
.box {
@include border-radius(3px);
}
编译后的css代码
.box {
-webkit-border-radius: 3px;
border-radius: 3px;
}
传一个带值的参数
@mixin border-radius($radius:3px){
-webkit-border-radius: $radius;
border-radius: $radius;
}
- 调用的时候不传参数值,则使用默认参数值
.btn {
@include border-radius;
}
编译后的css代码
.btn {
-webkit-border-radius: 3px;
border-radius: 3px;
}
- 调用的时候传参数值,则使用传进的参数值
.btn {
@include border-radius(50%);
}
编译后的css代码
.btn {
-webkit-border-radius: 50%;
border-radius: 50%;
}
传多个参数
/* 定义 mixin */
@mixin center($width,$height){
width: $width;
height: $height;
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
margin-top: -($height) / 2;
margin-left: -($width) / 2;
}
/* 调用 mixin */
.box-center {
@include center(500px,300px);
}
编译后的css代码
.box-center {
width: 500px;
height: 300px;
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
margin-top: -150px;
margin-left: -250px;
}
有一个特别的参数
…。当混合宏传的参数过多之时,可以使用参数来替代,如:
/* 定义 mixin */
@mixin box-shadow($shadows...){
@if length($shadows) >= 1 {
-webkit-box-shadow: $shadows;
box-shadow: $shadows;
} @else {
$shadows: 0 0 2px rgba(#000,.25);
-webkit-box-shadow: $shadow;
box-shadow: $shadow;
}
}
/* 调用 mixin */
.box {
@include box-shadow(0 0 1px rgba(#000,.5),0 0 2px rgba(#000,.2));
}
编译后的css代码
.box {
-webkit-box-shadow: 0 0 1px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5), 0 0 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
box-shadow: 0 0 1px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5), 0 0 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
}
mixin 的不足
Sass 在调用相同的混合宏时,并不能智能的将相同的样式代码块合并在一起
继承 extend
在 Sass 中是通过关键词 @extend 来继承已存在的类样式块,从而实现代码的继承。
.class1{
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
.class2{
@extend .class1;
font-size:16px;
}
编译后的css代码
.class1, .class2 {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
.class2 {
font-size: 16px;
}
占位符 %placeholder
%placeholder 声明的代码,如果不被 @extend 调用的话,不会产生任何代码。
%mt5 {
margin-top: 5px;
}
%pt5{
padding-top: 5px;
}
.btn {
@extend %mt5;
@extend %pt5;
}
.block {
@extend %mt5;
span {
@extend %pt5;
}
}
编译后的css代码
.btn, .block {
margin-top: 5px;
}
.btn, .block span {
padding-top: 5px;
}
混合宏、继承、占位符比较
字符串
- 有引号字符串(quoted strings)
- 无引号字符串(unquoted strings)
在编译css文件时,不会改变字符串的类型。
但是使用#{}插值语句(interpolation)时,有引号字符串会被编译为无引号字符串,这样方便在mixin中引用选择器名。
Sass运算
除法运算
/符号被当作除法运算符时有以下几种情况:
- 如果数值或它的任意部分是存储在一个变量中或是函数的返回值。
- 如果数值被圆括号包围。
- 如果数值是另一个数学表达式的一部分。
p {
font: 10px/8px; // 纯 CSS,不是除法运算
$width: 1000px; // 定义一个变量
width: $width/2; // 使用了变量,是除法运算
width: round(1.5)/2; // 使用了函数,是除法运算
height: (500px/2); // 使用了圆括号,是除法运算
margin-left: 5px + 8px/2px; // 使用了加(+)号,是除法运算
}
字符运算
- 有引号字符串在左,则加完还是有引号字符串
- 无引号字符串在左,则加完还是无引号字符串